If 2025 was the year of the “Chatbot,” 2026 is shaping up to be the year of the “Worker.” For the past 18 months, boardrooms and IT departments have been flooded with demonstrations of Large Language Models (LLMs) that can write poems or summarize emails. However, as the novelty wears off, CIOs are digging deeper to find high-impact Agentic AI Use Cases that deliver actual returns on investment rather than just interesting conversations.
Agentic AI matters for enterprises because it drives measurable outcomes. It enhances automation, improves workflow orchestration, and reduces inefficiencies across business functions like IT, HR, and finance. By enabling autonomous decision-making and seamless integration of systems, agentic AI drives measurable outcomes and operational efficiency.
This shift represents the “So What?” moment for enterprise AI. It is the moment where the hype cycle crashes into the reality of operational budgets. Stakeholders are no longer impressed by a tool that can talk about a problem; they want a tool that can fix it.
The Shift from Conversation to Action
This is exactly where Agentic AI distinguishes itself from the standard Generative AI tools we’ve grown accustomed to. When comparing agent capabilities, traditional AI systems like ChatGPT primarily analyze data and follow predefined instructions with human oversight. In contrast, purpose-built agentic AI systems can monitor data, identify patterns, and automate decision-making processes.
Agentic AI represents a new generation of artificial intelligence systems that go beyond simple automation or passive response. These intelligent systems are designed to make autonomous decisions and execute actions without waiting for explicit human instructions at every step. By interpreting data, learning from ongoing interactions, and adapting to new information, agentic AI solutions empower enterprises to automate complex processes and routine tasks that previously required significant human effort.
In this post, we are leaving the theoretical definitions behind. We will explore three concrete scenarios—across IT Operations, Finance, and Customer Success—that demonstrate how agentic AI works: these autonomous, proactive systems interpret data, make decisions, and perform tasks independently in real-world business scenarios.
Key Takeaways on Agentic AI Use Cases
- Beyond the Chatbot: We are shifting from AI that talks (Generative) to AI that acts (Agentic).
- Real ROI: The value of Agentic AI isn’t in novelty; it’s in reducing Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR), automating compliance, and preventing revenue churn. 92% of leaders expect that agentic AI will deliver measurable ROIwithin two years.
- Key Benefits: Agentic AI delivers improved efficiency, automation, and enhanced decision-making, making it a transformative technology for business and financial operations.
- Autonomy with Control: Effective agents don’t run wild; they operate within strict AI governance frameworks, logging their actions just like human employees.
- Versatility: From “self-healing” IT servers to “proactive” sales assistants, the use cases span the entire enterprise.
How Agentic AI Works in the Enterprise
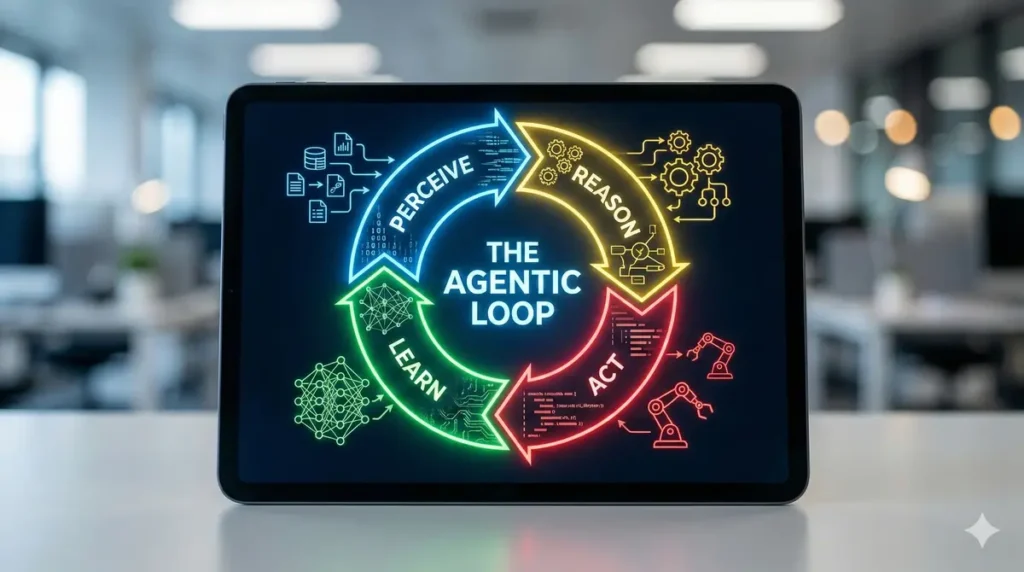
Agentic AI operates through a structured, multi-step process that enables it to interpret data, make informed decisions, and execute tasks with minimal human oversight. These advanced AI systems are seamlessly integrated with enterprise systems, giving them access to vast amounts of business data and operational signals. By leveraging technologies such as natural language processing and machine learning models, agentic AI tools can understand context, identify trends, and predict outcomes with impressive accuracy.
In practice, agentic AI tools automate routine tasks across a variety of business functions. For example:
- Sales teams can use agentic AI to automatically qualify leads and prioritize outreach.
- Customer support teams benefit from proactive support that anticipates and resolves issues before they escalate.
- Software development teams use agentic AI to streamline testing, debugging, and deployment processes.
AI Agents vs. Agentic AI
AI agents are specialized software programs designed to autonomously perform specific tasks, such as processing transactions or monitoring network activity.
Agentic AI extends the capabilities of these traditional agents by enabling them to collaborate, share information, and adapt to dynamic business environments. In agentic AI systems, multiple agents—each with their own area of expertise—work together to achieve complex objectives that would be difficult for a single agent or rule-based system to handle.
Why “Agentic AI Use Cases” Matter More Than “Tech Specs”
In the enterprise, technology is only as good as the problem it solves. We often get lost in discussions about context windows, parameters, and model weights, but the board only cares about outcomes.
Traditional AI approaches, such as rule-based systems, rely on static decision trees to dictate actions. In contrast, agentic AI systems move beyond these fixed rules, exhibiting greater autonomy and adaptability in problem-solving. This shift enables agentic AI to drive enterprise automation, proactively monitoring, diagnosing, and resolving issues across the enterprise infrastructure without human intervention.
The fundamental difference lies in agency. Standard AI is reactive; it requires a human to prompt it for every single step. Autonomous AI agents in enterprise environments are proactive. They monitor specific signals—a server alert, an invoice email, a customer behavior pattern—and execute a multi-step plan to resolve the issue.
This capability unlocks a cost-effective implementation strategy because it frees your human experts from “keeping the lights on” tasks, allowing them to focus on high-value strategic work.
Here is what that looks like in practice.
Use Case 1: The “Self-Healing” IT Infrastructure (IT Operations)

Every CIO knows the “2:00 AM Nightmare.” A critical application server runs out of disk space or hangs due to a memory leak. In the traditional model, this triggers a cascade of manual, expensive steps. Today, agentic AI leverages support systems and enterprise automation to proactively manage IT infrastructure, reducing downtime and manual intervention.
The “Old Way” (Manual): A monitoring tool sends an alert. The on-call engineer wakes up, logs into the VPN, investigates the issue, clears the temporary logs, restarts the service, and updates the ticket.
- Time: 2 hours.
- Cost: High stress, overtime pay, and potential SLA breaches.
The “Agentic Way” (Automated): An Agentic workflow is connected directly to the observability platform.
- Trigger: The monitoring system detects “Disk Space > 95%” on Server A.
- Action: The Agent receives the alert and initiates a diagnostic workflow, analyzing data from multiple systems to identify the root cause.
- Tool Use: It uses SSH to securely access the server. It runs a command to identify the largest files.
- Reasoning: It identifies that temp_error.log has grown abnormally large (20GB). It checks its policy: “Can I delete logs older than 7 days?” Yes.
- Execution: It archives the log file to S3 (cloud storage) for compliance, deletes the local copy, and restarts the service. The agent can execute multi-step workflows across multiple systems, orchestrating actions such as archiving, deletion, and service restarts without human intervention.
- Governance: It logs every command it runs into Jira or ServiceNow, tagging the ticket as “Resolved by AI Agent.”
The ROI: Zero human intervention for L1 support issues and a dramatic reduction in Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR). Agentic AI is transforming IT support by proactively identifying and resolving issues before they escalate. It enhances IT operations through automated incident detection and provisioning.
The Strategic Value of IT Agentic AI Use Cases
Deploying Agentic AI Use Cases in IT operations transforms the department from a cost center to a center of resilience. By automating the “fix,” your engineering talent is liberated to focus on architecture and innovation rather than firefighting. This is often the first place enterprises start because the variables are controlled and the data is structured, making it one of the most reliable Agentic AI Use Cases for immediate implementation.
Use Case 2: The “Intelligent” Procurement Auditor (Finance)

Procurement teams lose thousands of hours manually matching PDF invoices to Purchase Orders (POs) and battling “Maverick Spend.” While robotic process automation (RPA) can automate simple tasks based on predefined rules, agentic AI goes further by adapting to complex environments and making decisions autonomously.
The “Old Way” (Manual): An Accounts Payable (AP) clerk opens the PDF, types the data into the ERP, and stares at the screen to compare line items. If there is a mismatch, they email the vendor and wait.
The “Agentic Way” (Automated): An AI agent acts as a 24/7 auditor that sits between your email inbox and your ERP.
- Trigger: An email arrives in the invoices@company.com inbox.
- Action: The Agent uses OCR to read the PDF and extract line items. It can autonomously call on external tools to automate data extraction.
- Reasoning: It logs into the ERP system to look up the PO number. It performs a “3-Way Match” (Invoice vs. PO vs. Goods Receipt).
- Decision:
- If Matched: It posts the invoice for payment scheduling.
- If Mismatched: It notices the vendor charged $100 per unit, but the contract says $90. It drafts and sends an email to the vendor: “Dear Vendor, Line item 3 is priced at $100, but our contract PO states $90. Please clarify.”
- Escalation: It flags the discrepancy to the Finance Manager, presenting the draft email for approval.
The ROI: This is AI agent workflow automation at its finest. Agentic AI is optimizing decision-making and automating complex processes by analyzing large volumes of data in real-time. It ensures 100% compliance with contract terms while humans only touch the exceptions.
Expanding Financial Agentic AI Use Cases
While invoice matching is a prime starting point, financial Agentic AI Use Cases extend to fraud detection, regulatory reporting, and dynamic forecasting. The ability of an agent to cross-reference unstructured data (like email contracts) with structured data (like ERP records) creates a level of auditability that manual processes cannot match. This demonstrates why financial Agentic AI Use Cases are becoming crucial for modern governance.
Use Case 3: The “Proactive” Customer Success Manager (Sales)
Customer churn is the silent killer of revenue. Usually, businesses are reactive—they only reach out to a client after the client has cancelled. Today, agentic AI leverages customer data to proactively manage customer success, identifying risks before they escalate.
The “Old Way” (Reactive): An Account Manager checks a dashboard once a month. They realize “Client X” hasn’t logged in for two weeks. They call the client, but it’s often too late.
The “Agentic Way” (Proactive): An Agent, acting as an AI assistant and autonomous team member, monitors user behavior in real-time to detect “Churn Risk” signals.
- Trigger: Usage data shows that “Client X” hasn’t used a key feature (e.g., “Reporting”) in 14 days.
- Action: The Agent identifies this pattern as a risk, helping manage rising ticket volumes by addressing issues before they escalate.
- Tool Use: It queries the company’s Knowledge Base to find a tutorial specifically about “Reporting.”
- Execution: It drafts a personalized email from the Account Manager’s address: “Hi [Name], I noticed you haven’t run a report lately. Here is a 2-minute video that shows how to automate that step.”
- Follow-up: It updates the status in Salesforce/HubSpot to “At Risk” and tasks the human manager to call if no reply is received within 48 hours.
The ROI: Revenue protection. This is one of the clearest Agentic AI vs. Generative AI examples. Generative AI could write the email, but only Agentic AI knows when to send it and who to send it to. By 2026, autonomous agents in Customer Experience are expected to resolve roughly 80% of routine issues.
Customer-Centric Agentic AI Use Cases
Proactive churn management is just one of many customer-facing Agentic AI Use Cases that drive retention. By integrating CRM data with communication tools, agents can handle renewals, upsells, and onboarding support autonomously. These Agentic AI Use Cases don’t just save time; they fundamentally improve the customer experience by ensuring no client ever falls through the cracks due to human oversight.
How to Identify Your First Use Case
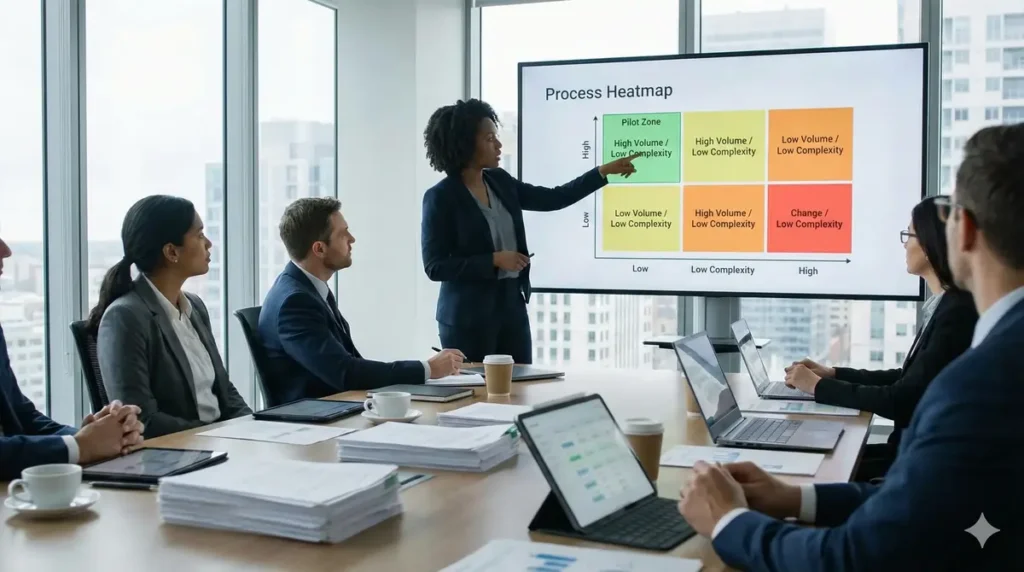

You don’t need to overhaul your entire organization overnight. The key to a successful pilot is to start small but meaningful. When evaluating potential agentic AI use cases, remember that successful deployment requires careful customization and integration into your existing business infrastructure.
Look for processes that are:
- High Volume: Tasks that happen dozens or hundreds of times a week.
- Rules-Based: Workflows where the decision logic is clear.
- Data-Rich: Processes where the inputs are digital (logs, emails, database records).
Selecting the Right Agentic AI Solution
Selecting the right agentic AI solution is critical for maximizing the benefits of autonomous systems within your organization. Start by clearly defining the business problem you want to solve and the level of autonomy required. The ideal agentic AI solution should integrate smoothly with your existing enterprise systems, support transparent and explainable decision-making, and be scalable to accommodate future growth.
Implementing agentic AI solutions
Implementing agentic AI solutions requires a thoughtful, structured approach. Assess your current processes to determine where autonomous systems can deliver the most value. Once you have identified a candidate, use the Pilot to Production roadmap to execute it safely. By following these best practices, businesses can minimize risks and maximize the benefits of agentic AI.
Conclusion: The Future is Autonomous
We are moving away from AI as a “Co-pilot” (who sits next to you) to AI as an “Agent” (who goes and does the work for you). Agentic AI systems can autonomously complete tasks from start to finish, understanding instructions, making decisions, and executing actions independently.
This transition will define the next decade of enterprise IT. Agentic AI enables organizations to handle growing data and workloads without proportional increases in headcount, thanks to scalable automation. The organizations that win won’t be the ones with the best chatbots; they will be the ones that successfully deploy and scale their Agentic AI Use Cases to automate the mundane, liberate their workforce, and execute at machine speed.
Is your organization ready to move beyond the chatbot?
At Blue Phakwe Consulting, we specialize in helping enterprises identify high-impact Agentic AI Use Cases that deliver measurable ROI without compromising governance.
Contact us today to schedule your initial consultation and map out your first pilot.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the main difference between a Chatbot and an AI Agent?
A chatbot is passive; it waits for a human prompt to generate text. An AI Agent is active; it can perceive its environment, make decisions based on goals, and use tools (like email, CRMs, or code) to complete a task without constant human hand-holding.
2. Are Agentic AI use cases safe for regulated industries?
Yes, provided they are built with the right governance. Most organizations implement bounded autonomy, where AI agents operate within defined limits and require human approval for high-risk decisions. Bounded models of Agentic AI require traceable decision logs to meet regulatory standards.
3. How do I choose my first Agentic AI use case?
Look for processes that are high-volume, repetitive, and rules-based. The best starting point is often a task that your team finds “boring but necessary,” such as resetting passwords or reconciling invoices. In cybersecurity, security teams benefit from agentic AI, which improves cybersecurity by autonomously identifying and mitigating threats in real-time. Agentic AI can also simplify cybersecurity case management by automating the classification, tracking, and resolution of security incidents.
4. Do I need a massive data science team to build this?
Not necessarily. The ecosystem is evolving rapidly. Many Agentic AI use cases can now be built using low-code platforms or by leveraging existing APIs from major cloud providers, making them accessible even to mid-sized enterprises.



